Health Benefits of Fennel Seeds

Fennel, a Mediterranean vegetable with a distinctive licorice flavor, offers culinary versatility. Its bulb, leaves, and seeds are all edible, finding use in global cuisines. The bulb can be enjoyed cooked or raw, while the seeds serve as a flavorful spice for baked goods, meats, and drinks.

In addition to its other nutrients, fennel also provides a range of essential minerals and vitamins, including phosphorus, zinc, copper, manganese, selenium, niacin, pantothenic acid, folate, choline, beta-carotene, lutein, zeaxanthin, vitamin E, and vitamin K.
Health Benefits
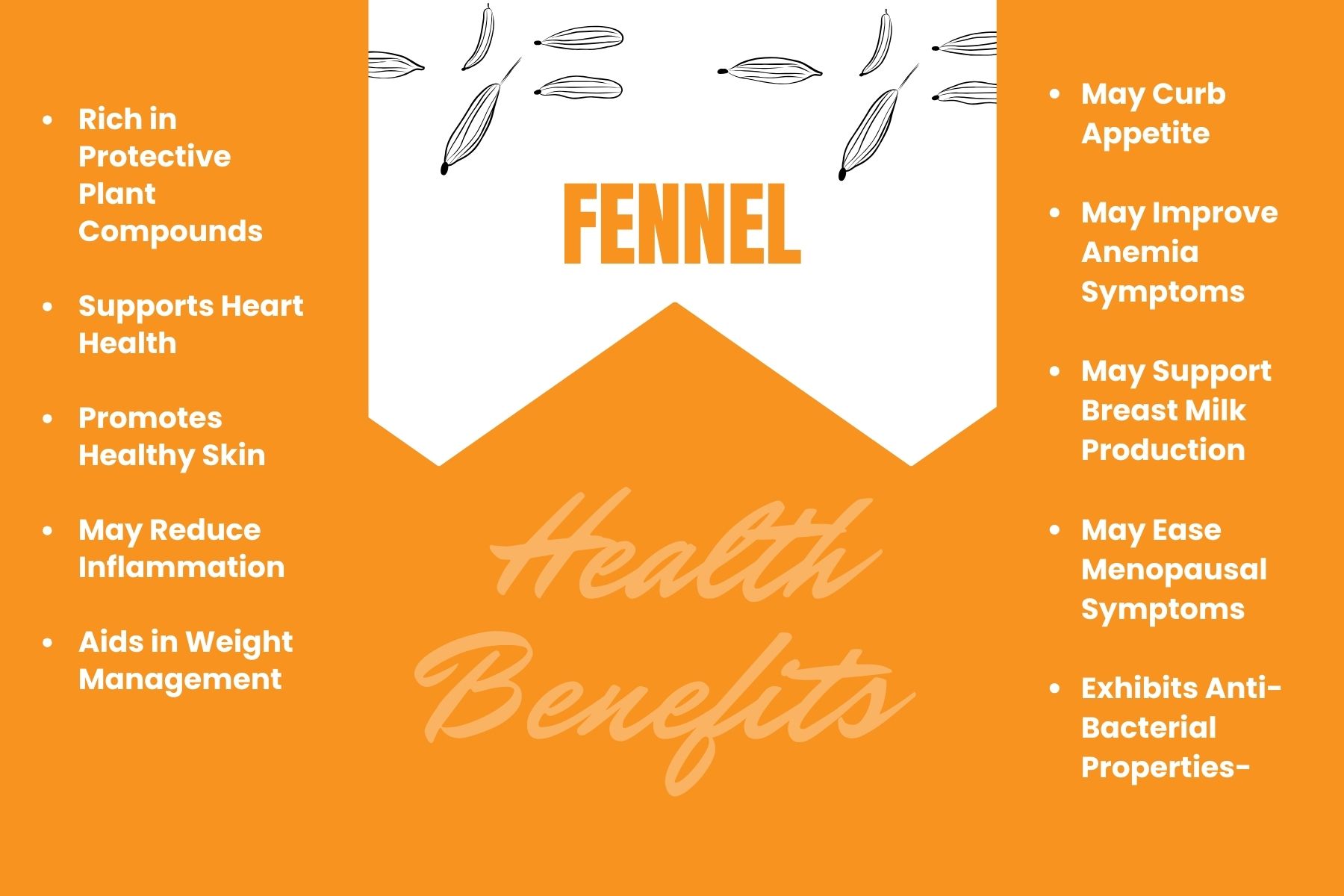
- Rich in Protective Plant Compounds– Fennel is packed with compounds like chlorogenic acid, limonene, and quercetin, which may lower the risk of chronic diseases.
- Supports Heart Health– Its fiber, potassium, and folate content may help manage cholesterol, lower blood pressure, and promote cardiovascular well-being.
- Promotes Healthy Skin– Beta-carotene (vitamin A) and vitamin C in fennel contribute to collagen production and tissue repair, benefiting skin and mucous membranes.
- May Reduce Inflammation– Antioxidants like vitamin C and quercetin in fennel may help combat inflammation.
- Aids in Weight Management– Low in calories and high in fiber, fennel can help regulate blood sugar and support weight management efforts.
- May Curb Appetite– The compound anethole in fennel may help suppress appetite, although more research is needed to confirm this effect.
- May Improve Anemia Symptoms– Fennel’s folate content supports red blood cell formation, potentially alleviating anemia symptoms.
- May Support Breast Milk Production– Anethole in fennel may increase breast milk quality and quantity by promoting prolactin production, but more research is needed.
- May Ease Menopausal Symptoms– Fennel extract may alleviate menopausal symptoms like hot flashes and sleep disturbances, though further studies are warranted.
- Exhibits Anti-Bacterial Properties– Fennel extract may inhibit the growth of harmful microbes like E. coli and Staphylococcus aureus.
Using Fennel in Diet
Adding fennel to your diet is easy and delicious. Its crunchy texture and mild sweetness work well in both raw and cooked dishes. When shopping, select firm fennel bulbs with a pale green or white color, avoiding any with spots or bruises. Fresh stalks should be green, and leaves should be tightly bundled.
To prepare fennel, remove the stalks and slice the bulb vertically. Then, get creative. Use the stalks for flavorful soup stock, sauté the leaves and stalks with onions for a quick side, add sliced fennel to salads for a crisp bite, or roast the bulbs for a satisfying entrée. Store dried fennel seeds in an airtight container for optimal freshness.
Include It in Daily Diet as Fennel Tea
Fennel tea offers several potential health benefits. Its antiviral properties may support the body’s response to colds. It can aid digestion, freshen breath, and promote relaxation, potentially contributing to better sleep.
Safety Concerns
While fennel is generally safe for most people as part of a balanced diet, there are some important considerations.
Individuals with celery or carrot allergies may also experience allergic reactions to fennel. Pregnant women, infants, and babies should avoid fennel seeds, tea, and extracts due to potential safety concerns. Fennel’s phytoestrogenic properties could disrupt maternal hormones and may not be safe for infants. Concentrated forms of fennel, like extracts and supplements, should always be used with caution and under professional guidance.
