Plant-Based Diets for Weight Loss

Plant-based diets have grown in popularity, driven by concerns for environmental sustainability and the potential health benefits they offer. Studies have linked these diets to improved heart health, a reduced risk of diabetes, and even increased longevity. Weight loss is another significant advantage often acknowledged.
While a plant-centric approach can certainly support weight management goals, it’s important to understand that simply eliminating animal products isn’t a magic bullet. A diet loaded with processed vegan foods like ‘Oreos’ and soda will hardly contribute to weight loss.
Scientific Research on Plant-Based Diets and Weight Loss
A growing body of scientific evidence supports the role of plant-based diets in weight management. A comprehensive review published in Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome, and Obesity found that these diets can effectively promote weight loss across various populations, including individuals with overweight, type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and rheumatoid arthritis.
Further research, as published in the Journal of Geriatric Cardiology, demonstrated that individuals sticking to plant-based diets generally exhibited lower body mass index (BMI) compared to those with non-plant-based diets.
“Several recent meta-analyses point to the superiority of vegetarian diets over non-vegetarian diets as a weight loss strategy,” emphasizes Carol Johnston, PhD, RD, a professor of nutrition at Arizona State University. However, the exact mechanisms behind this weight loss advantage remain a subject of debate.
“The basis for successful weight loss lies in a sustained calorie deficit,” Dr. Johnston clarifies. “This can be achieved through various strategies, such as reducing consumption of processed foods, high-fat foods, and high-sugar foods,” all of which are typically minimized in a healthy, whole-foods plant-based diet.
Plant-Based Diets in Weight Loss and Improved Health
Obesity has reached epidemic levels worldwide, with a significant portion of the adult population struggling with being overweight or obese.
Fortunately, adopting a healthier lifestyle, including dietary changes, can effectively promote weight loss and improve overall health.
Numerous studies have demonstrated the efficacy of plant-based diets for weight management. These diets, characterized by their high fiber content and exclusion of processed foods, create a favorable environment for shedding excess kilos.
A comprehensive review of 12 studies involving over 1,100 participants revealed that individuals following plant-based diets experienced significantly greater weight loss (approximately 4.5 kilos) compared to those on non-vegetarian diets over an 18-week period.
Plant-based diets have also shown effect in maintaining long-term weight loss. A study in individuals with overweight or obesity showed that those on a whole-foods, plant-based (WFPB) diet not only lost more weight than the control group but also sustained this weight loss (approximately 25 kilos) over a year.
It’s important to note that the control group in this study may not have received any specific dietary guidance.
Nevertheless, simply eliminating processed foods, such as soda, candy, fast food, and refined grains, which are typically restricted on a WFPB diet, can be a powerful strategy for weight loss.
Health Benefits of a Plant-Based Diet
A whole-foods, plant-based (WFPB) diet offers numerous health benefits beyond weight loss.
Heart Health
A large-scale study involving over 200,000 individuals demonstrated that adhering to a healthy WFPB diet – rich in vegetables, fruits, whole grains, legumes, and nuts – significantly reduced the risk of developing heart disease. Conversely, less nutritious plant-based diets high in sugary drinks, fruit juices, and refined grains were linked to a slightly increased risk.
Cancer Prevention
Research suggests a potential link between plant-based diets and a reduced risk of certain cancers. Studies have shown a possible association between a healthy WFPB diet and lower risks of breast cancer and aggressive forms of prostate cancer. Additionally, a 2022 review indicated that plant-based diets may be linked to a reduced risk of digestive system cancers, including pancreatic, colon, rectal, and colorectal cancers.
Cognitive Health
Plant-based diets, abundant in antioxidants and plant compounds, may play a role in protecting cognitive function and slowing the progression of Alzheimer’s disease. Numerous studies have linked higher fruit and vegetable consumption to a reduced risk of cognitive decline and dementia.
Diabetes Management
A WFPB diet can be a valuable tool for diabetes prevention and management. Studies have shown that individuals adhering to a healthy plant-based diet have a significantly lower risk of developing diabetes. Moreover, plant-based diets have been shown to improve blood sugar control, body weight, and cholesterol levels in individuals with diabetes.
Tips for Beginners to Lose Weight on a Plant-Based Diet
Interested in trying out a plant-based diet for weight loss? Follow these tips to start with.
- Define Your Plant-Based Path
There’s no fixed approach to plant-based eating. Explore options like veganism, vegetarianism (lacto-ovo, pescatarian), or even flexitarianism (incorporate some animal products). Research shows that all these approaches can support weight loss. Consider how each option aligns with your lifestyle and social habits.
- Take a Gradual Approach
Don’t feel pressured to go completely plant-based overnight. Start by slowly incorporating more plant-based meals into your routine. For example, begin by adding more vegetables to your existing meals and swapping out desserts for fresh fruit. A 2019 study in Frontiers in Nutrition found that consuming whole fruits can contribute to weight management.
- Explore Plant-Based Swaps
Learn about plant-based alternatives of common animal products. Experiment with different types of plant-based protein sources and learn how to use ingredients like flaxseed to replace eggs in baking. Many plant-based swaps offer lower calorie and fat content compared to their animal counterparts. For example, tofu contains significantly fewer calories than chicken breast, and almond milk has fewer calories and fat than cow’s milk.
- Prioritize Protein
Ensure you’re getting enough protein from plant-based sources such as beans, legumes, tofu, seitan, and tempeh. While plant protein doesn’t necessarily have an advantage over animal protein for weight loss, studies indicate that adequate protein intake is crucial for successful weight management.
- Keep Meal Planning Simple
Don’t over complicate your meals. Start with easy-to-prepare options like stir-fries with frozen vegetables and pre-cooked rice. A study in Annals of Behavioral Medicine found that meal planning is associated with lower BMI.
- Focus on Satiety
Include protein and fiber in every meal to keep you feeling full and satisfied throughout the day. This will help you avoid overeating.
- Read Food Labels
Be mindful of processed plant-based foods. Read labels carefully to avoid excessive saturated fat, added sugar, and sodium. Remember, even plant-based foods can be unhealthy if they are highly processed.
Barriers to Weight Loss on a Vegetarian Diet
While vegetarianism can be a powerful tool for weight management, several factors can be a hindrance to weight loss efforts.
What are these?
- Overconsumption and Insufficient Protein
Even healthy vegetarian meals can lead to weight gain if you consume excessive portions. Sufficient protein intake is important for weight management. Protein increases satiety by reducing ghrelin levels, a hormone that stimulates hunger. Insufficient protein intake can lead to increased food consumption to compensate.
- Excessive Refined Carbohydrate Consumption
Overconsumption of refined carbohydrates, such as white bread, pasta, and sugary cereals, can hinder weight loss. These foods are often low in fiber and may not effectively curb hunger, leading to increased calorie intake. Refined carbs can trigger an insulin surge, which may contribute to weight gain.
- Overindulging in High-Calorie Plant Foods
While healthy fats from nuts, seeds, avocados, and coconut oil are essential, they are high in calories (9 calories per gram). Overconsumption of these foods can lead to excess calorie intake. It’s important to be mindful of portion sizes when consuming calorie-dense plant-based foods.
- Reliance on Processed Foods
Many processed vegetarian foods, such as veggie burgers, meat substitutes, and packaged meals, contain high levels of sodium, added sugars, and unhealthy additives. Excessive consumption of these processed foods can contribute to weight gain and increase the risk of other health issues.
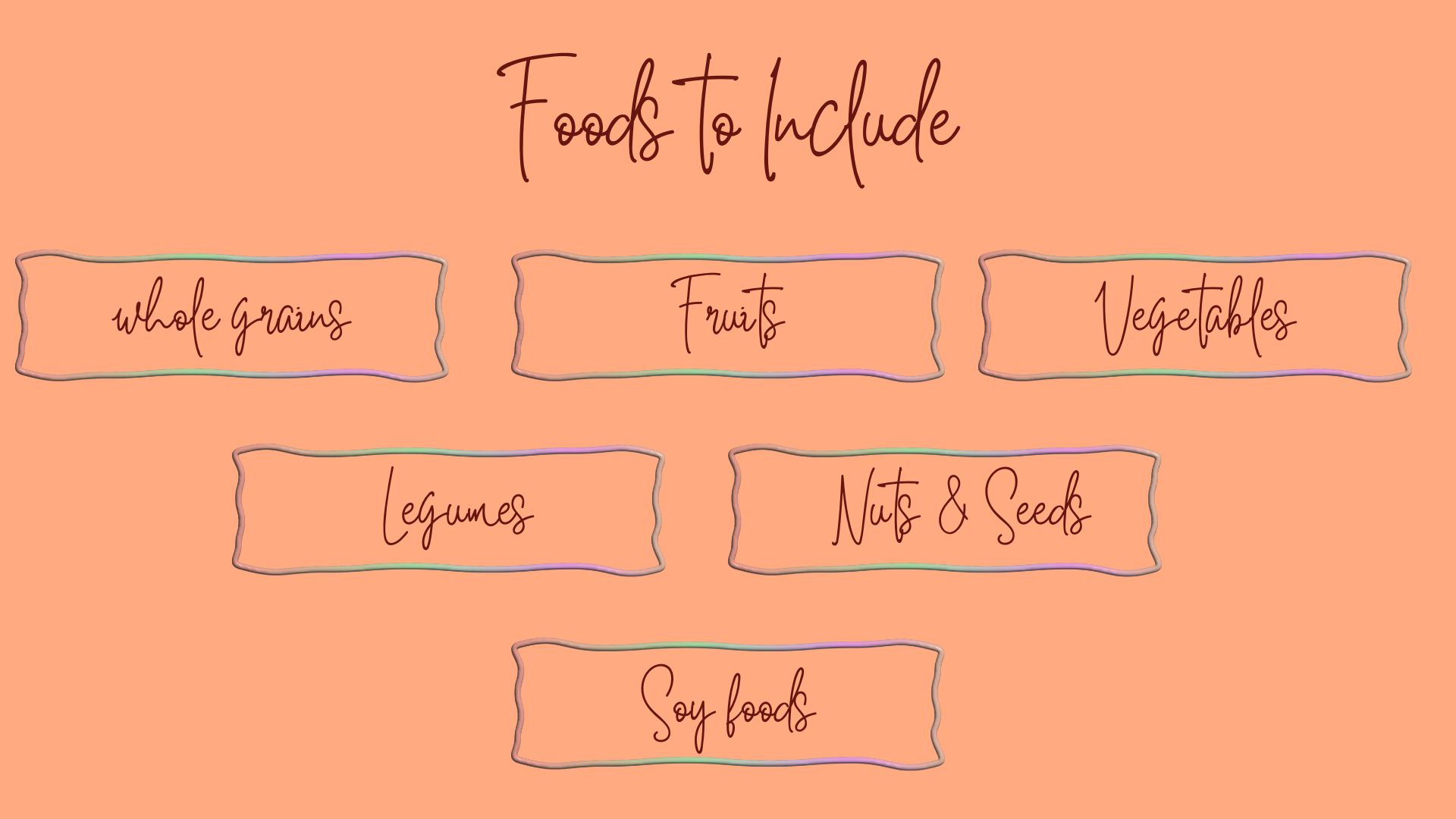
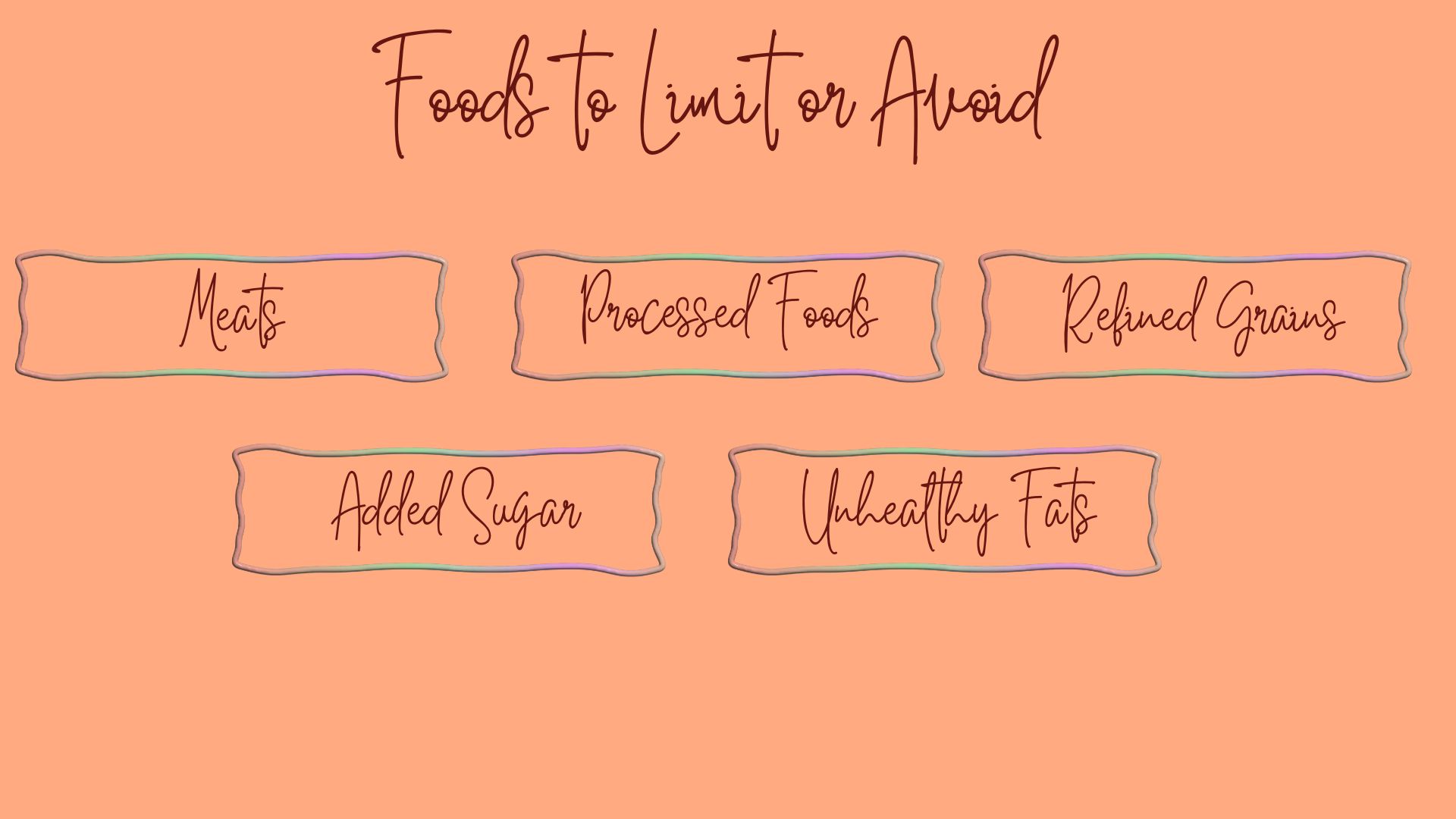
Foods to Eat / Avoid on a Plant-Based Diet
Contrary to popular belief, a plant-based diet is far from just “rabbit food.” Depending on your chosen path (vegan, vegetarian, pescatarian), you can enjoy a diverse range of delicious and nutritious options.
Here’s a list of what to prioritize and what to limit when following a plant-based diet for weight loss, based on the research discussed earlier.
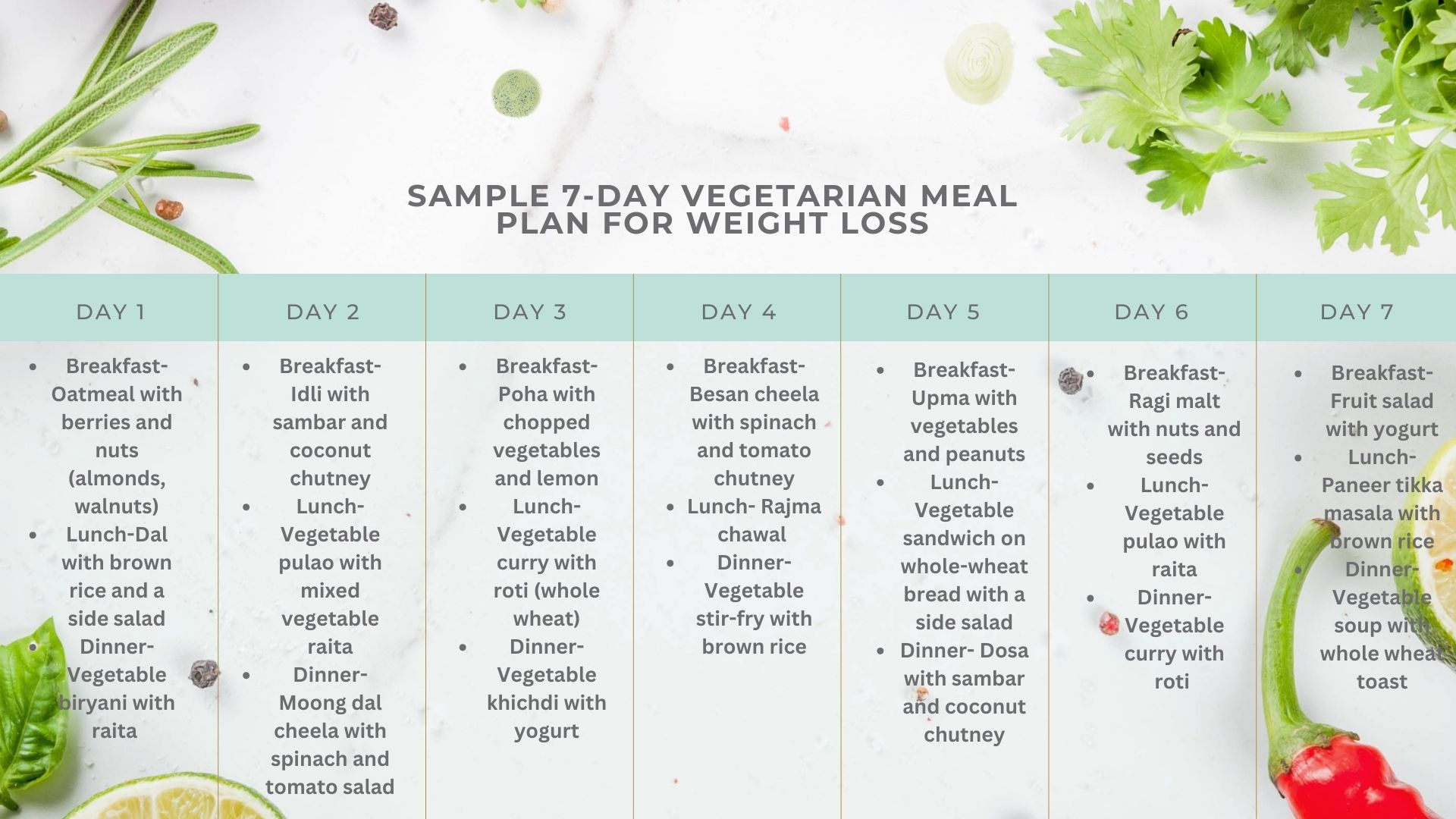
A Sample Meal Plan
Disclaimer- This is a sample plan and may need to be adjusted based on individual needs and preferences. Consult a registered dietitian for personalized guidance.
A whole-foods, plant-based diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, minimizes animal products and processed foods. This approach is linked to numerous health benefits, including reduced risk of heart disease, certain cancers, and chronic conditions like diabetes. Plus, it’s environmentally friendly. So, if you want to lose weight and stay fit, you can definitely give this a try.
